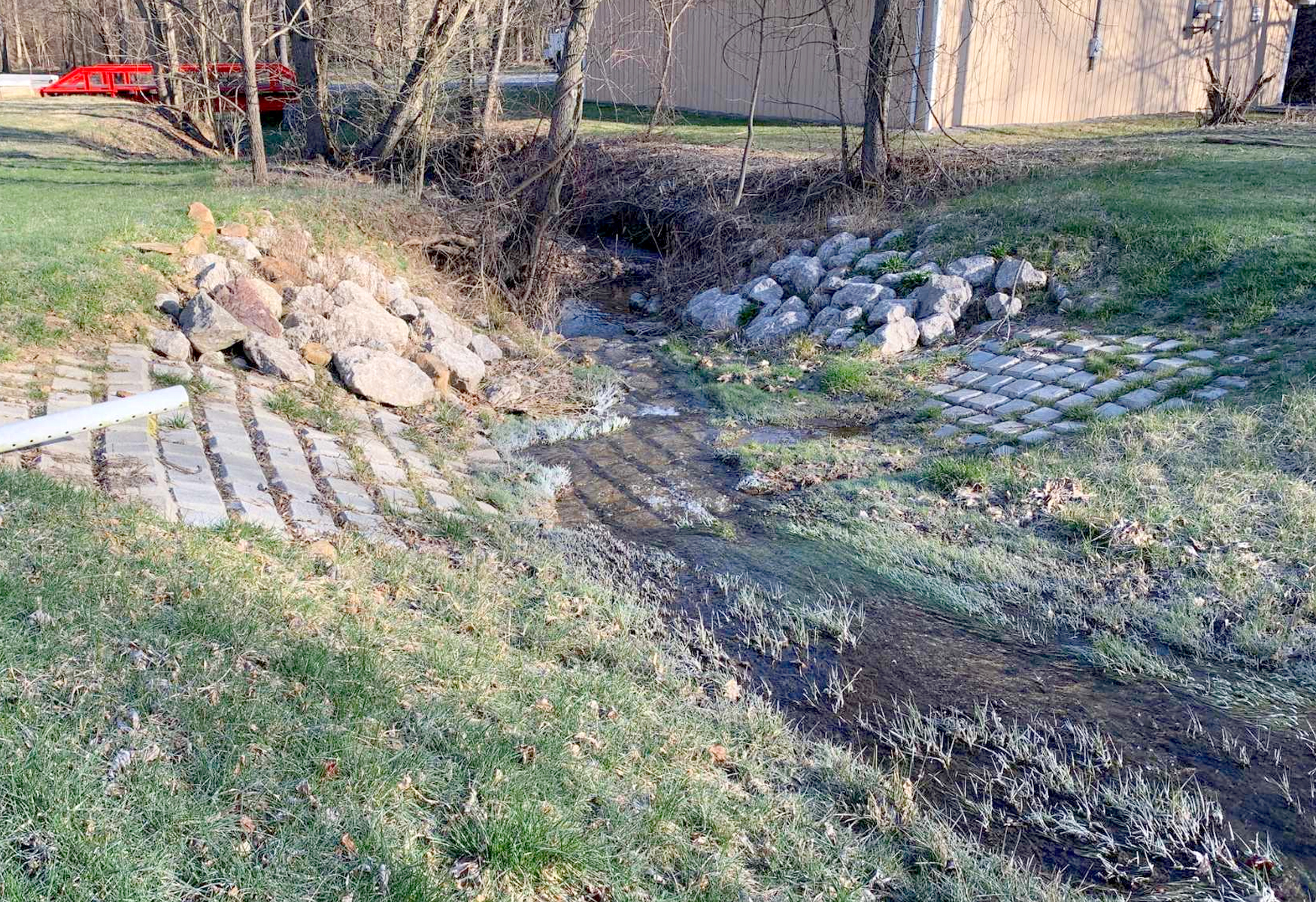
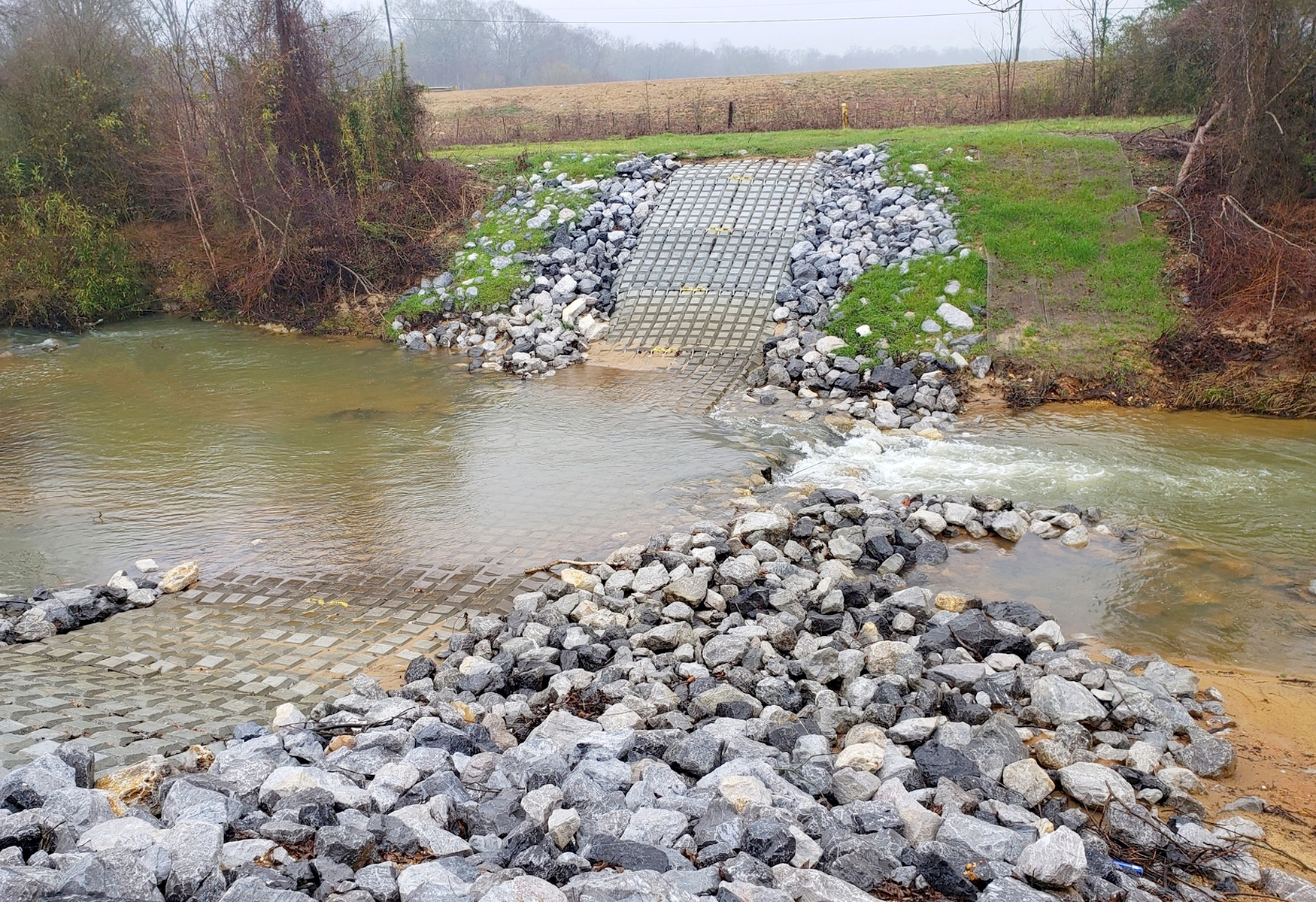
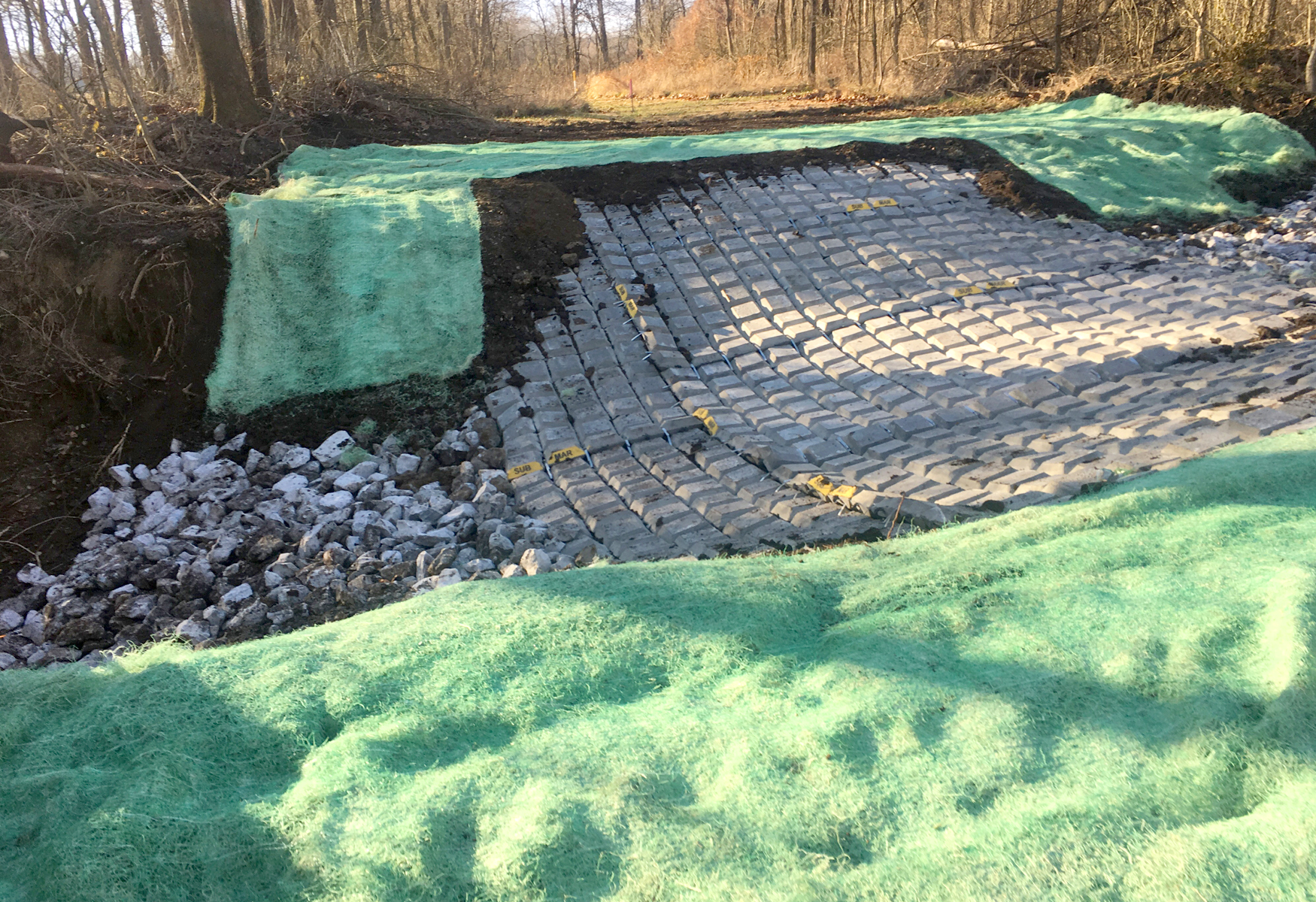
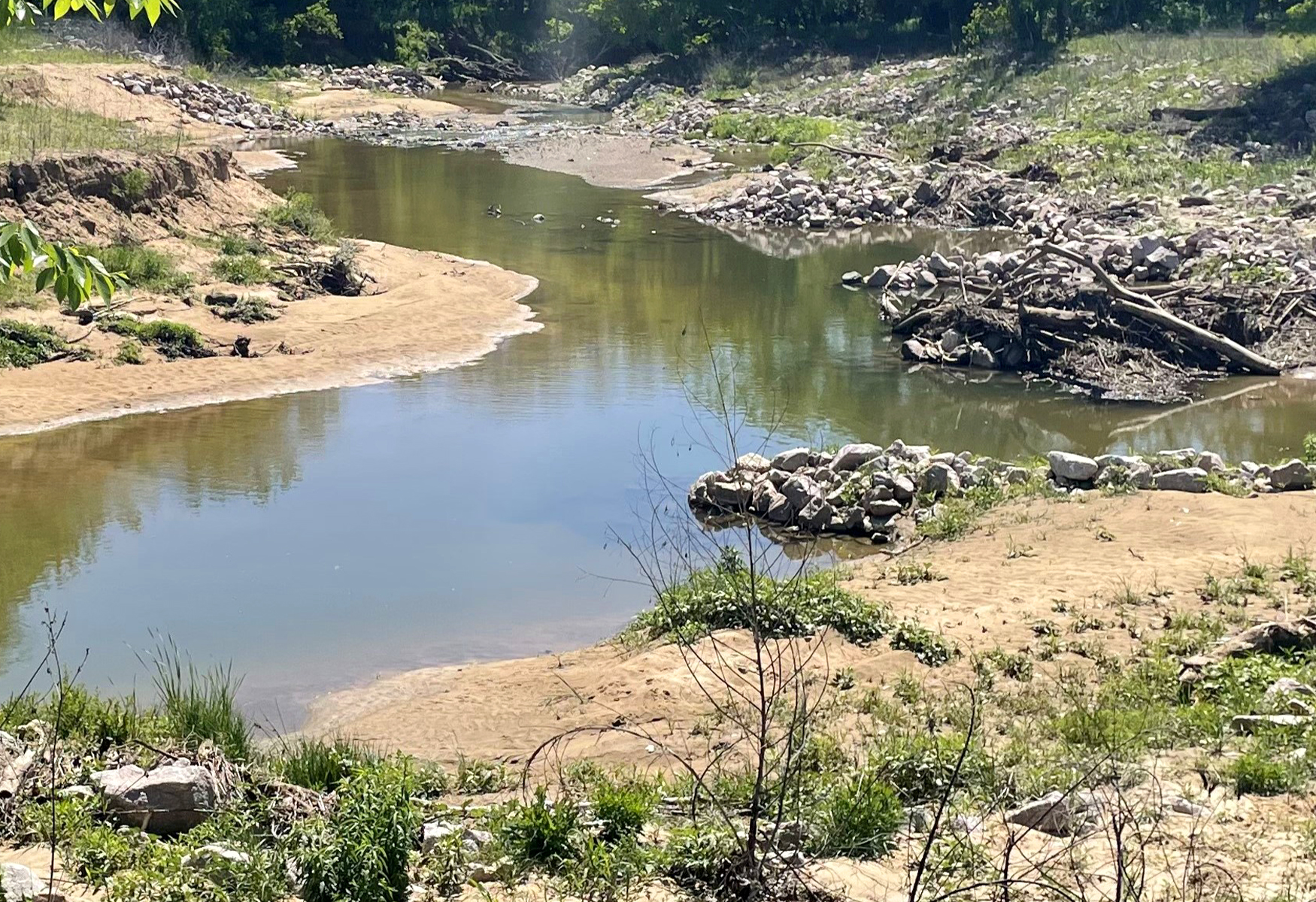
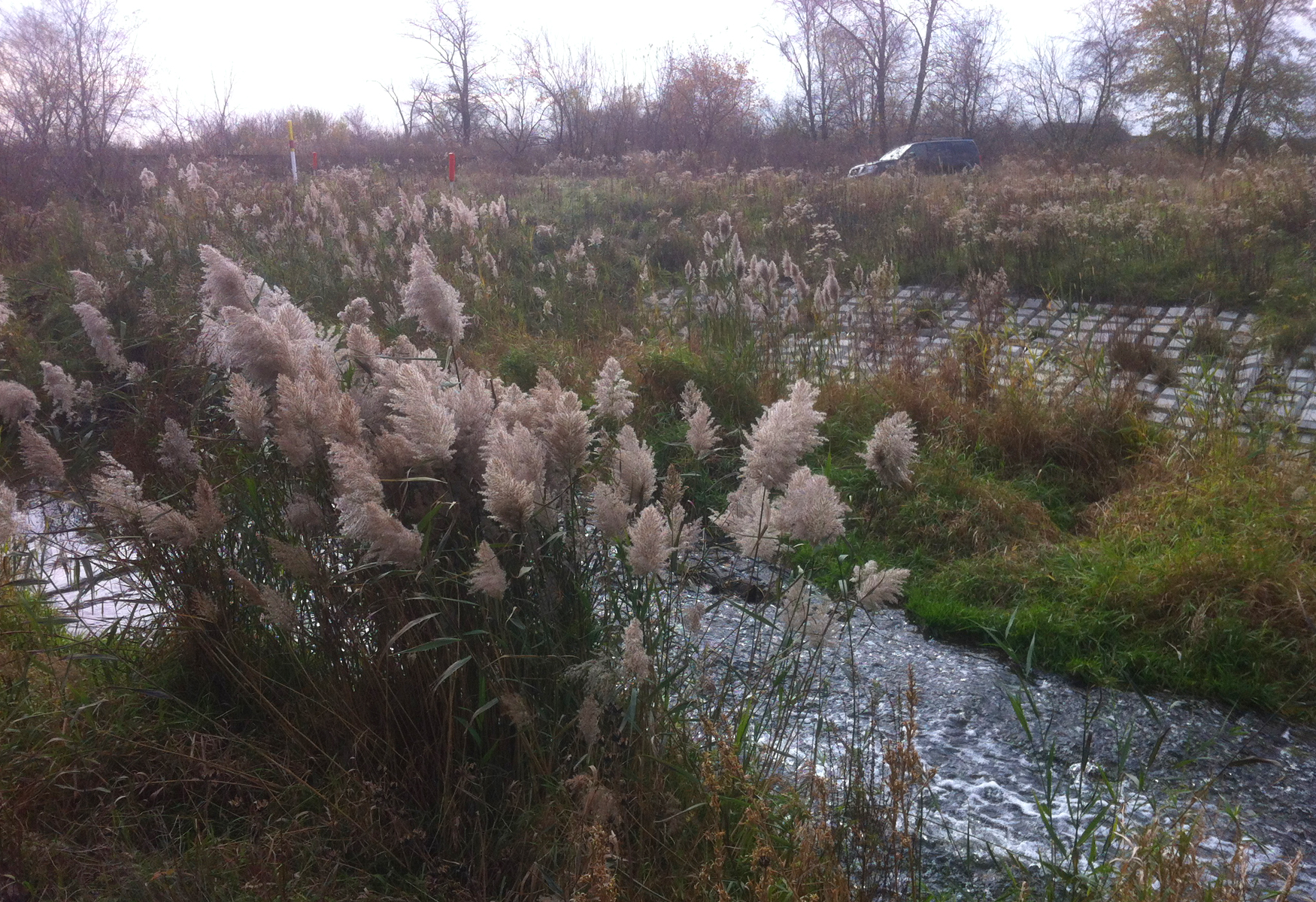
A 10-inch natural gas pipeline crosses a tributary to Dilworth Run in Beaver County, Pennsylvania in a 25-foot wide right-of-way. The soil is composed of clay with rock in the channel bed and well-vegetated banks.
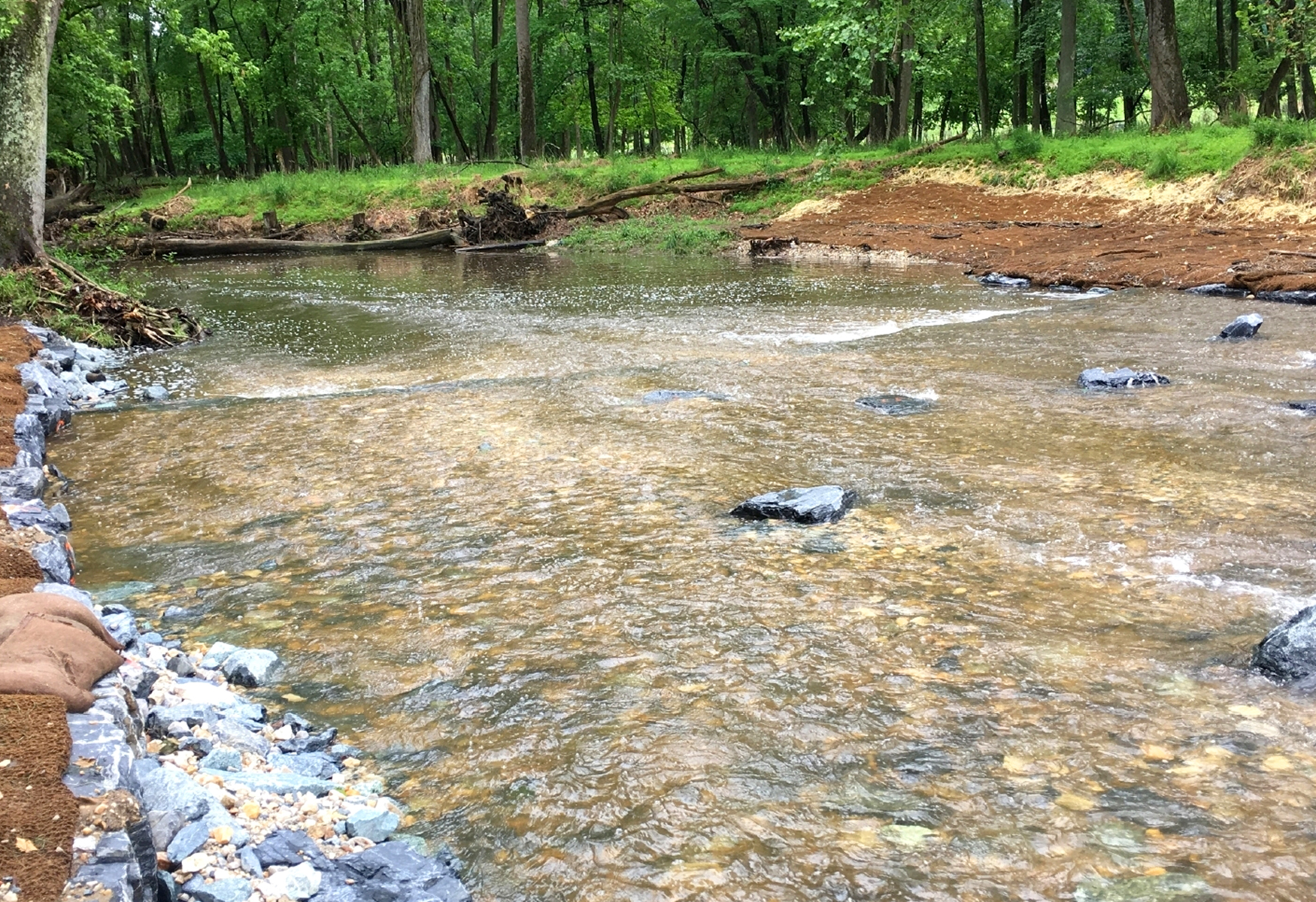
A 24-inch natural gas pipeline crosses Little Mulberry Creek in Chilton County, Alabama in a 50-foot wide right-of-way. The soil in the creek bed is composed of clay and sand, and the banks are well-vegetated with trees and grass.
A 10-inch diameter natural gas pipeline crosses a tributary to Big Blue River in Indiana. A headcut -- an abrupt drop in the bed of the channel -- developed in a small drain that flows into Big Blue River and has exposed the pipeline for approximately 11 linear feet and left it suspended for approximately 12 linear feet.
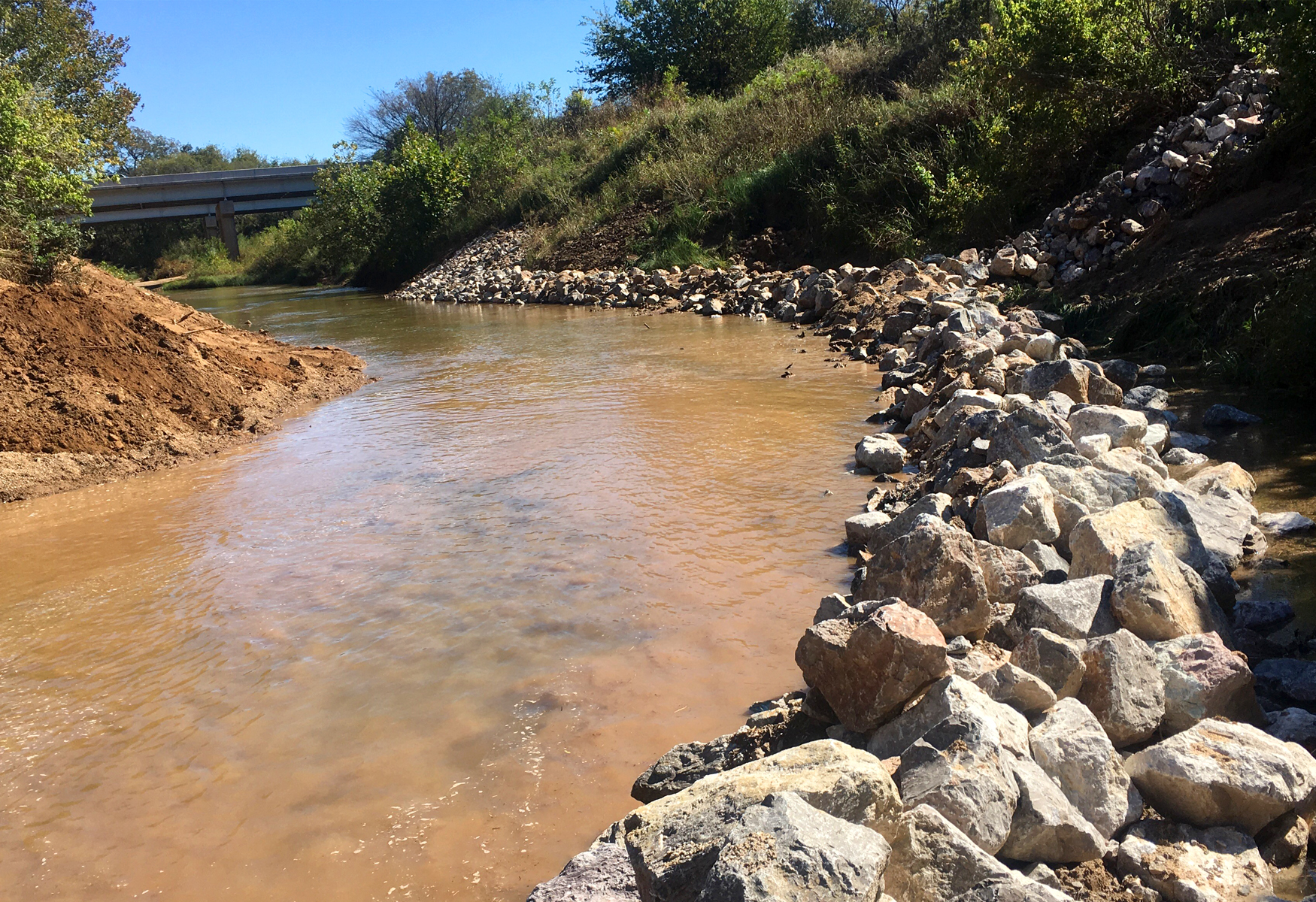
A 20-inch natural gas pipeline crosses Little Sandy Creek in Pontotoc County, Oklahoma. The creek bed is composed of clay, sand, gravel, and riprap. Broken concrete was previously placed on the right-descending bank but has scattered.
A 50-foot wide pipeline right-of-way contained an 18-inch refined product pipeline. The 18-inch pipeline crosses Dyer Ditch between a railroad corridor and a residential area in Lake County, Indiana. Downcutting of the creek bed caused the banks to become steep and unstable...
A 22-inch diameter natural gas pipeline that crosses the northwest branch of the Anacostia River in Silver Spring, MD, had become exposed due to bank erosion and lateral migration of the channel. Previously placed rock failed to remediate the erosion issue.
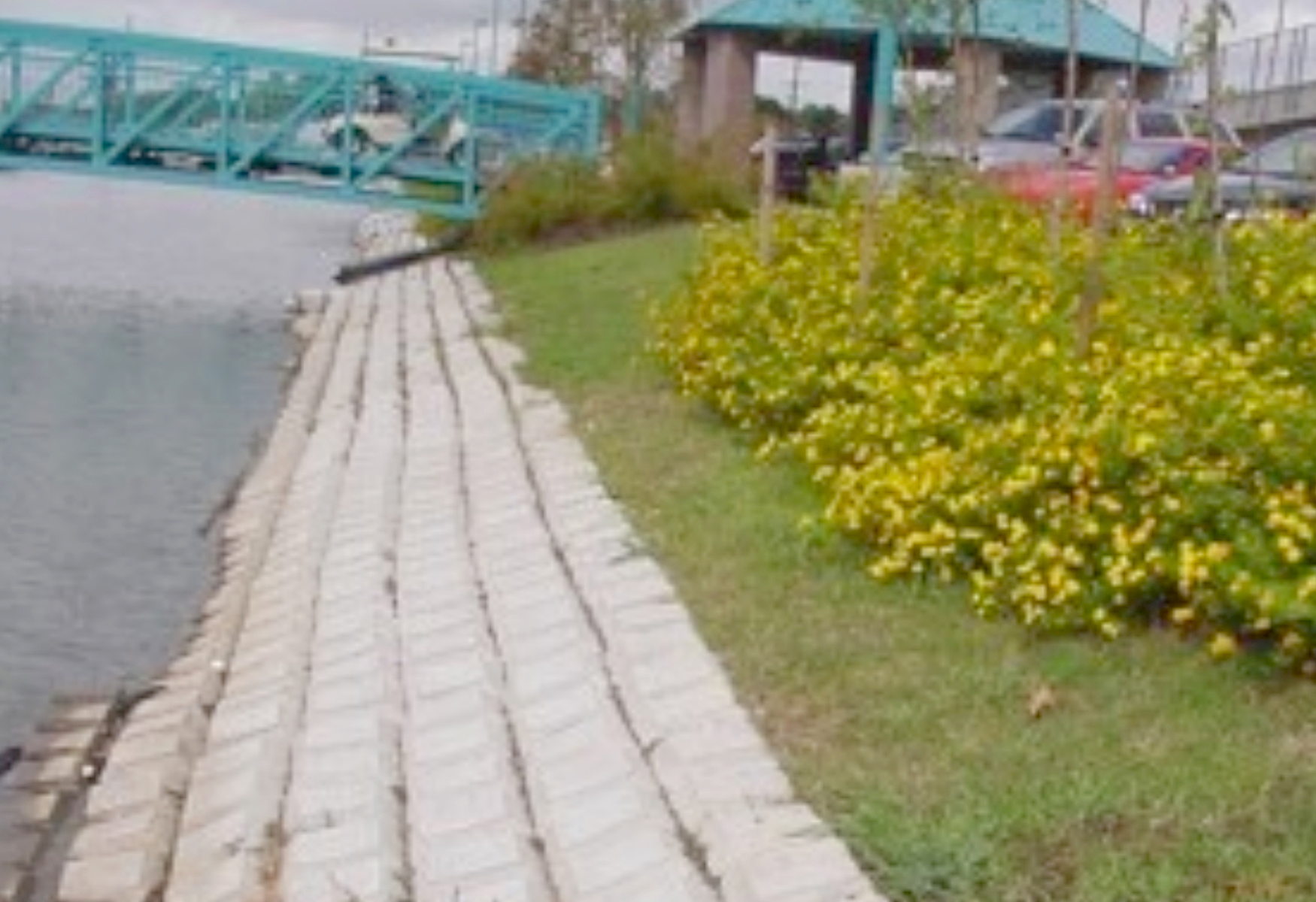
The Terrebonne General Medical Center planned a bank stabilization and beautification project along Bayou Terrebonne in Terrebonne Parish, Louisiana. The plan included installation of a 100 ft steel arch pedestrian bridge across Bayou Terrebonne from East Main Street to East Park Avenue.
An 8-inch natural gas pipeline crosses Caddo Creek in Carter County, Oklahoma. The bed and banks of the creek are composed of clay and sand and the banks are well vegetated. Heavy rain caused lateral migration and head cutting that eroded the right descending bank.